Method Overloading
- In object-oriented programming languages, method overloading enables a class to have several methods with the same name but different parameters.
- However, in Python, method overloading is not directly supported as opposed to languages such as Java or C++. This is because Python allows developers to define default arguments for their methods and pass arguments of any type to a method. This flexibility allows a single method to handle various types of arguments, eliminating the need for overloading.
- However, there is a way to simulate method overloading in Python by using default argument values or variable length arguments and conditional statements. Here's an example:
Program
using default arguments:
Program
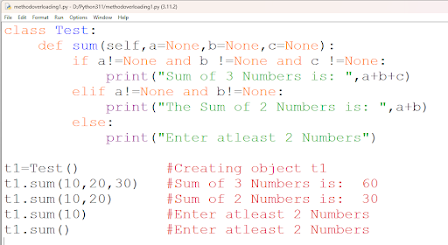
using variable length arguments:
Multiple
methods with Same Name:
- When we define multiple methods with same name, Python will consider the last defined method only.
- Python will not support method overloading. (Why? Method overloading features are already builtin)
- Constructor overloading also not supported by python. If we try constructor method overloading, only last constructor is considered)
Method Overriding
Method
overriding is a feature in object-oriented programming that allows a subclass
to provide a different implementation of a method that is already defined in its
superclass.
In
Python, when a subclass defines a method with the same name as a method in its
superclass, the subclass method "overrides" the superclass method.
This means that when an object of the subclass calls the overridden method, it
will execute the implementation provided by the subclass instead of the
implementation provided by the superclass.
Example:
class Shape:
def area(self):
print("Area not defined for this shape")
class Circle(Shape):
def __init__(self, radius):
self.radius = radius
def area(self):
print("Area of Circle:", 3.14*self.radius**2)
class Rectangle(Shape):
def __init__(self, length, width):
self.length = length
self.width = width
def area(self):
print("Area of Rectangle:", self.length*self.width)
s = Shape()
s.area() # Output: Area not defined for this shape
c = Circle(5)
c.area() # Output: Area of Circle: 78.5
r = Rectangle(4, 6)
r.area() # Output: Area of Rectangle: 24
In
this example, we have a superclass Shape with a area() method that prints
"Area not defined for this shape". The subclasses Circle and
Rectangle override the area() method with their own implementations that
calculate the area of the respective shapes.
When we create an object of the Shape class and call the area() method, it prints "Area not defined for this shape" because the superclass implementation does not have a definition for area.
When we create an object of the Circle class and call the area() method, it prints the area of the circle because the subclass implementation has overridden the superclass implementation with its own formula.
Similarly, when we create an object of the Rectangle class and call the area() method, it prints the area of the rectangle because the subclass implementation has overridden the superclass implementation with its own formula.
Method
Overriding vs Method Overloading
Method
overriding and method overloading are both object-oriented programming
concepts, but they differ in how they allow us to define methods with the same
name.
Method
overriding allows a subclass to provide a different implementation of a method
that is already defined in its superclass. This means that when an object of
the subclass calls the overridden method, it will execute the implementation
provided by the subclass instead of the implementation provided by the
superclass.
Method
overloading, on the other hand, allows us to define multiple methods with the
same name in a class, but with different parameters. This means that we can
have a method with the same name in a class that performs different tasks
depending on the number or type of parameters passed to it.
Self
Assessment Questions:
Method
Overloading:
- What is method overloading?
- Which programming languages support method overloading?
- Why does Python not support method overloading by default?
- How can we simulate method overloading in Python?
Method
Overriding:
- What is method overriding?
- What is the difference between method overriding and method overloading?
- Why is method overriding used in object-oriented programming?
- What happens when a subclass overrides a method of its superclass?
- Give an example of method overriding in Python.
· \

Comments
Post a Comment